Effective Rice Bug Control for Optimal Farming Success
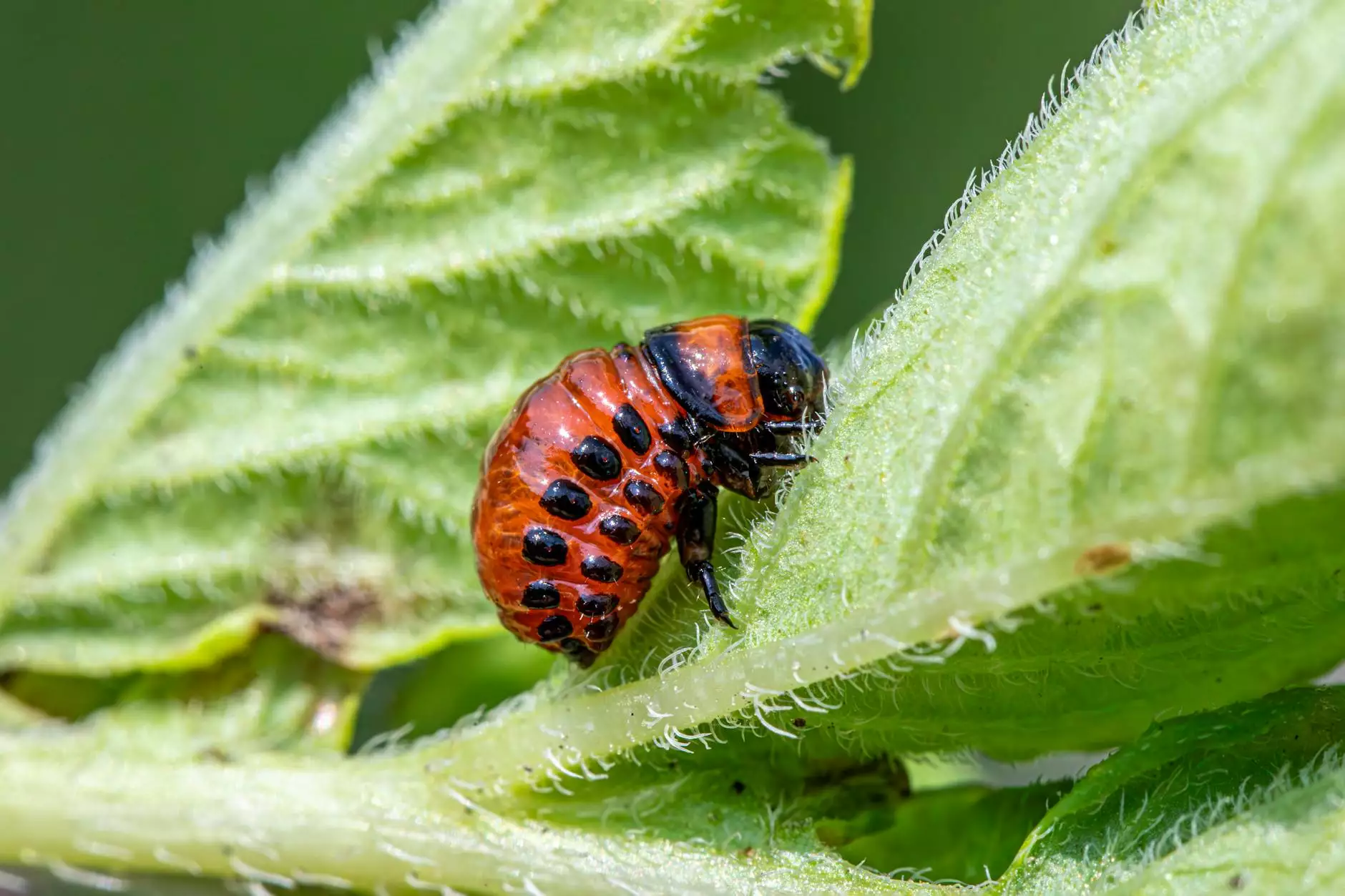

When it comes to rice bug control, farmers face various challenges that can significantly impact their crop yield. Rice bugs, particularly the notorious Leptocorisa oratorius (commonly known as the rice bug or rice leaf bug), can wreak havoc on rice fields. Understanding how to effectively manage these pests is crucial for maintaining healthy crops and maximizing productivity.
The Importance of Rice Bug Control
Farmers must prioritize rice bug control due to the pest's potential to damage rice plants at multiple stages of growth. This involves understanding their life cycle, feeding patterns, and the environmental conditions that contribute to their proliferation. The following points highlight the significance of controlling rice bugs:
- Preventing Crop Loss: Untreated infestations can lead to severe yield losses.
- Maintaining Quality: Bugs can damage grains, resulting in poor quality produce.
- Protecting Investment: Effective pest control safeguards the financial investment made in crops and resources.
- Ensuring Sustainable Practices: Managing pests sustainably helps protect the ecosystem and promotes biodiversity.
Understanding Rice Bugs
Before delving into effective control methods, it is essential to understand the biology and behavior of rice bugs. These pests are primarily sucking insects, feeding on the plant sap, which can lead to:
1. Plant Stress
Prolonged feeding can cause stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and ultimately, death of the plant.
2. Grain Damage
Rice bugs can pierce the grains, leading to shriveling and discoloration, making them unmarketable.
3. Disease Transmission
In addition to direct damage, they can also transmit pathogens, worsening the crop's health.
Effective Strategies for Rice Bug Control
To establish a successful rice bug control program, a combination of cultural, mechanical, biological, and chemical strategies should be employed.
Cultural Control Methods
Cultural control methods focus on changing farming practices to make the environment less conducive to rice bug infestations.
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops can disrupt the life cycle of rice bugs and reduce their population.
- Water Management: Implementing proper irrigation practices can deter rice bugs, as they prefer certain moisture levels.
- Field Hygiene: Keeping fields clean and free of debris can reduce hiding spots for rice bugs.
- Planting Dates: Adjusting planting schedules may help avoid peak rice bug populations.
Mechanical Control Methods
Mechanical controls involve physical means to remove or eliminate rice bugs from the field.
- Hand-Picking: In small-scale farming, hand-picking insects can be effective for initial infestations.
- Traps: Sticky traps can catch adult rice bugs and reduce their numbers significantly.
- Row Covers: Floating row covers can protect young plants from insect attacks.
Biological Control Methods
Utilizing natural predators is a highly effective approach to controlling rice bugs without chemicals.
- Nematodes: Beneficial nematodes can target rice bugs at the larval stage.
- Predatory Insects: Introduce predatory insects such as spiders, ladybugs, or lacewings, which feed on rice bugs.
- Microbial Insecticides: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a natural bacterium that can effectively control various insect larvae.
Chemical Control Methods
When infestations are severe, chemical control may be necessary. However, it is crucial to choose options that are safe for the environment and non-target species.
- Insecticides: Selective insecticides can target rice bugs while causing minimal harm to beneficial insects.
- Timing of Application: Apply chemicals during the early life stages of rice bugs for better efficacy.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Combine chemical and non-chemical methods to minimize insecticide use.
Monitoring and Assessment
Continuous monitoring is vital for effective rice bug control. Implement the following practices to assess pest populations and determine the necessity for action:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct weekly inspections of plants, particularly during the peak development phase.
- Sampling Techniques: Use methods such as sweep netting or visual counts to estimate bug populations.
- Threshold Levels: Establish action thresholds based on economic considerations and the crop's growth stage.
Fostering Healthy Crop Environments
In addition to direct rice bug control techniques, fostering a healthy crop environment can mitigate pest issues. Consider the following practices:
- Soil Health: Healthy soil promotes robust plant growth, making them less susceptible to insect infestations.
- Diversity: Planting a diverse range of crops can confuse pests and disrupt their life cycles.
- Companion Planting: Use specific companion plants that repel rice bugs or attract beneficial insects.
Conclusion: Empowering Farmers through Effective Rice Bug Control
Managing rice bugs effectively is crucial for maximizing the potential of rice farming. By understanding their biology, implementing a mix of control methods, and fostering healthy crop environments, farmers can protect their investments, ensure high-quality yields, and enhance long-term agricultural sustainability. Remember, the key to successful rice bug control lies in a comprehensive, integrated approach that prioritizes both efficiency and environmental health.
For more information on rice bug control and other agricultural solutions, visit tsgcinc.com. Our team is dedicated to providing the best resources and support for farmers in need of effective farm equipment repair and farming equipment solutions.